|
Tagging Proteasome Subunits |
|
|
|
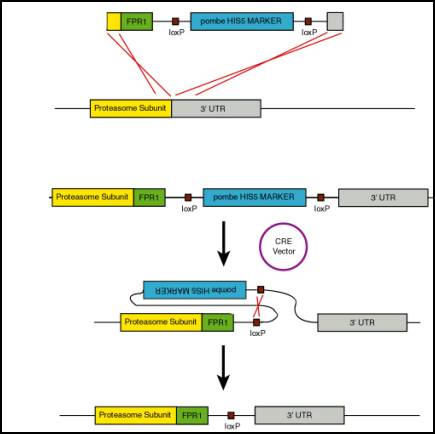
pUG-spHIS5 was obtained from
Stephen Oliver at the University of Manchester. The HIS5 marker from
S. pombe is flanked by loxP sites allowing for the excision of the marker
with cre- recombinase once the proteasome subunits were tagged with FPR1HA. FPR1 was amplified by PCR from the strain FY4 and subcloned
into the plasmid pUG-spHIS5 with a C-terminal HA-tag, forming pUG-spHIS5-FPR1HA.
Integration primers pairs were designed for tagging each of four proteasome
subunits (PRE10, RPN2, RPN6, RPN11). For each
pair, one primer contained 40 bp of genomic homology to the 3’ end of the
proteasome subunit, excluding the stop codon, and 20 bp of homology to the 5’
of FPR1 on pUG-spHIS5, excluding ATG. The second primer
contained 40 bp of genomic homology approximately 50 bp downstream of the
proteasome subunit gene stop codon and 20 bp of homology to pUG-spHIS5
immediately downstream of the spHIS5 marker flanked by loxP
sites. Two confirmatory primers were also designed that flanked the
integration site of each proteasome subunit. Strain
DY001 was transformed with pSH47, a plasmid with a galactose-inducible cre
gene and a URA3 selection marker. A 2 kb linear fragment from pUG-spHIS5-FPR1HA
was amplified using each integration primer pair to generate linear 2 kb fragments
suitable for genomic integration. 15 mg of each fragment was transformed into DY001 carrying
pSH47 and selection was performed on SC-URA-HIS. Colonies were then picked
and streaked onto SC-URA GAL to induce cre and to select for the
loopout of the spHIS5 marker. Colonies were finally streaked onto a
5-fluoroorotic acid containing plate to remove pSH47. All tagged subunits
were verified by sequencing. |